- 91-7208045555
- heartclinic999@gmail.com
- Mumbai, Maharashtra, India
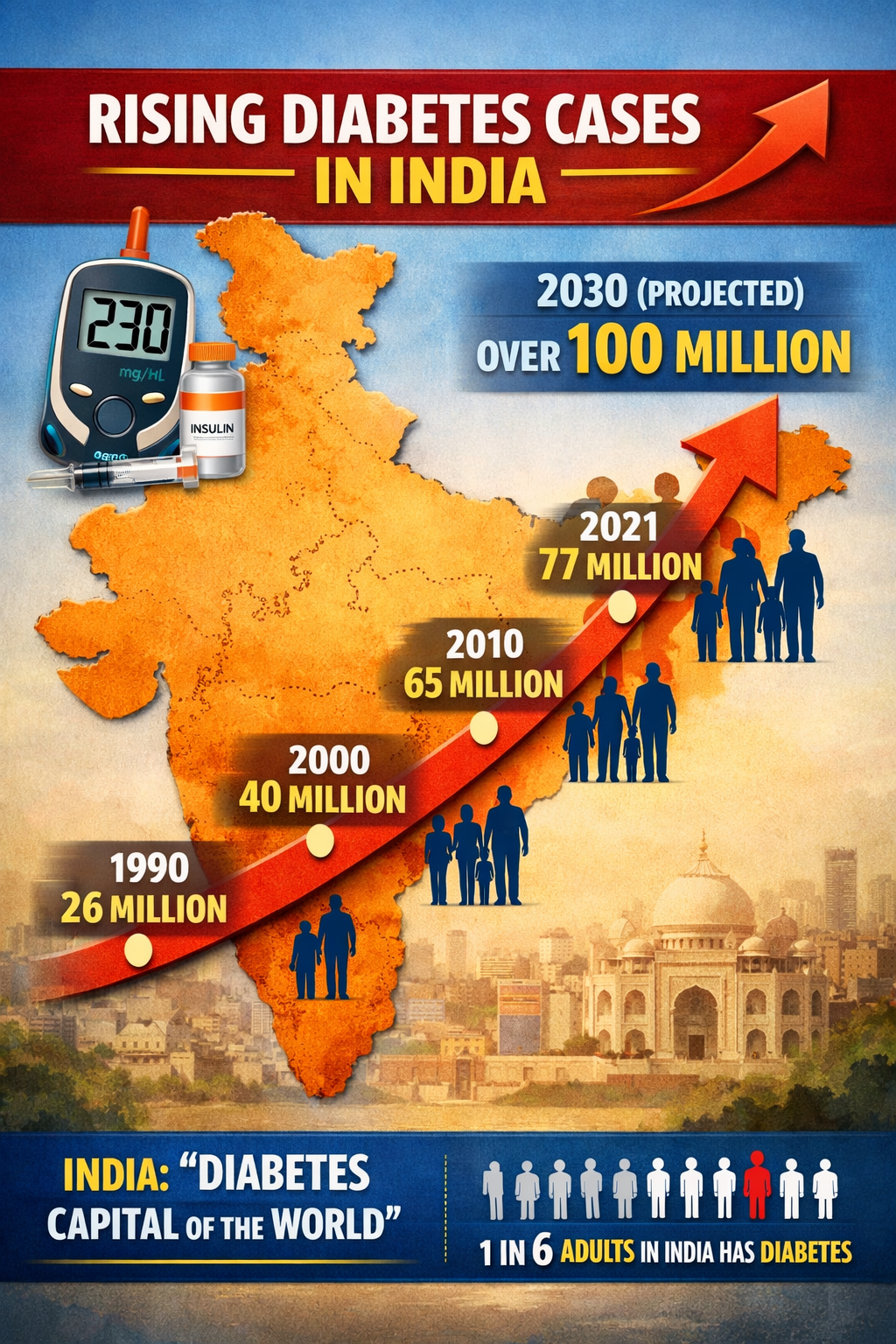
Multiple cohort and mechanistic studies consistently confirm that insulin resistance precedes hyperglycaemia by several years and represents the central driver of type 2 diabetes in Indians.