- 91-7208045555
- heartclinic999@gmail.com
- Mumbai, Maharashtra, India
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) remains the leading cause of mortality worldwide, accounting for approximately 32% of all global deaths. Coronary heart disease (CHD) constitutes the largest share of this burden.
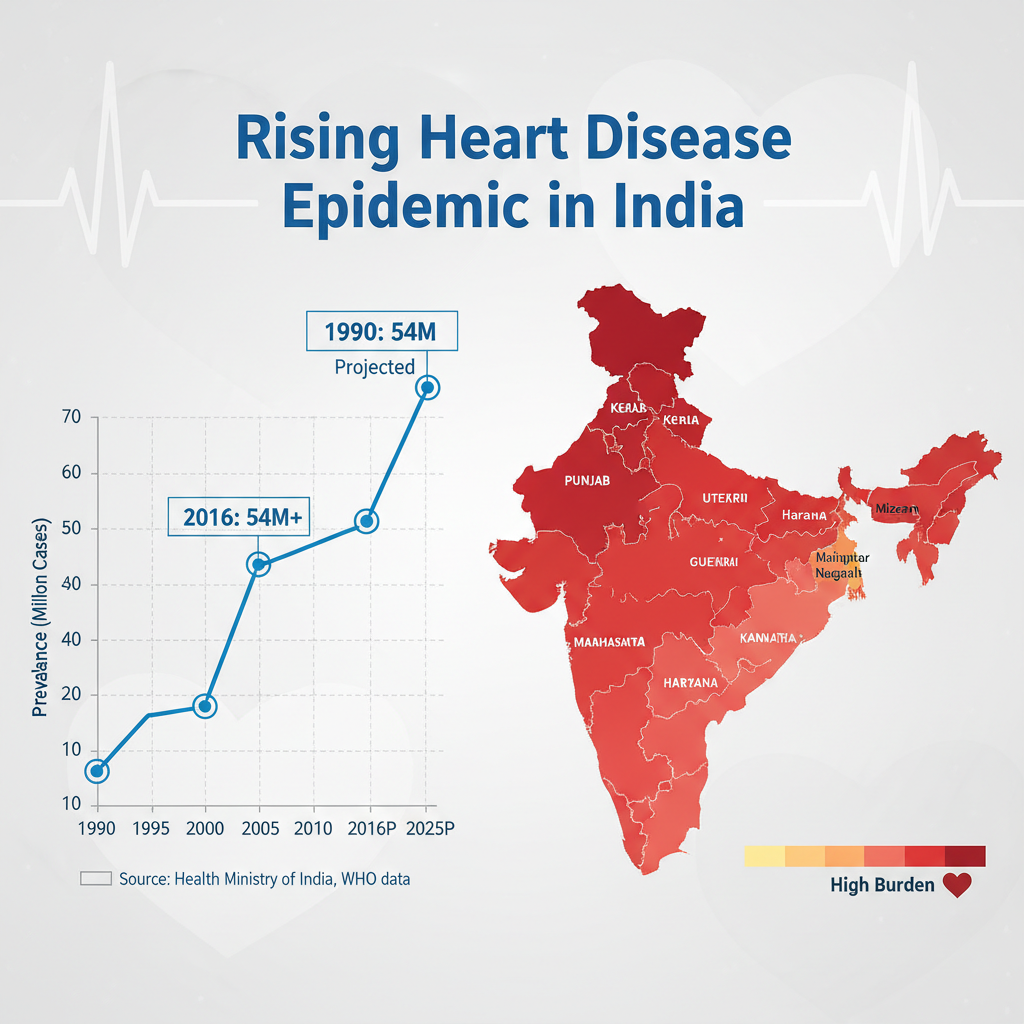
South Asians are disproportionately affected. Atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) occurs 5–10 years earlier, with higher mortality at lower BMI and LDL-C levels compared with Western populations.
Key insight: Traditional risk factors alone do not fully explain this excess risk in Indians. Metabolic risk is central.
These factors determine baseline susceptibility but are not directly actionable.
Dyslipidaemia & Hypertension
METS-IR
TyG Index
Heart disease is fundamentally a cardiometabolic disorder, driven by insulin resistance and visceral adiposity, with dyslipidaemia acting as a downstream mediator.

